Georgia 2026 Tax Changes — What Residents & Business Owners Must Know
- W-2 earners in Atlanta, Savannah, Augusta, Columbus, Macon
- Small business owners, LLCs, S-Corps, and freelancers
- Teachers, state employees, and healthcare professionals
- Families with children
- Retirees drawing from IRAs or pensions
- Real estate investors, landlords, and STR operators
This guide explains what Georgians need to know — and how to prepare before 2026 arrives.
Federal Tax Changes That Affect Georgia Residents
Below are the primary federal adjustments Georgians should prepare for.
Standard Deduction Shrinks in 2026
Many Georgians — particularly homeowners, families, and dual-income earners — will see higher taxable income at the federal level.
Commonly affected areas include Atlanta suburbs, Savannah, Augusta, and growing metros across the state.
Federal Tax Brackets Increase
- 12% rises to 15%
- 22% rises to 28%
- 24% rises to 31%
- Dual-income families
- Teachers and healthcare professionals
- Government and military households
- Professionals in Atlanta’s growing tech sector
- Households earning between $60,000–$250,000
QBI (20% Business Deduction) Remains Federal, but Georgia Does Not Mirror It
The federal QBI deduction remains in place.
Meaning:
- Federal taxable income decreases for qualifying business owners
- Georgia taxable income does not receive the same 20% reduction
- Georgia pass-through business owners must plan for this difference
This is particularly relevant for:
- Consultants
- Independent contractors
- Real estate agents
- Skilled trades
- Small LLCs and S-Corps
- Online business owners
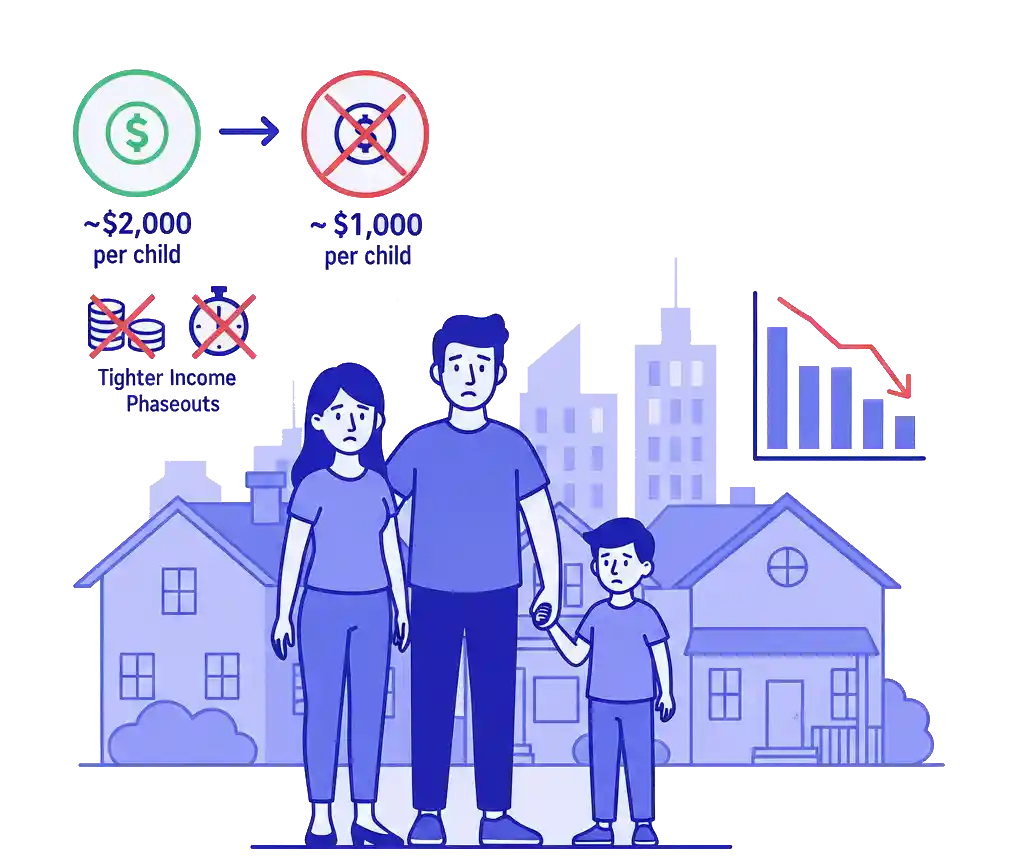
Child Tax Credit Shrinks
- From about $2,000 per child
- To about $1,000 per child
- Smaller refunds
- More families owing tax at filing time
This will affect many Georgia families, especially in suburban and growing population centers.
Marriage Penalty Returns
Georgia has a large population of dual-income households.
- Married filing jointly returns to older bracket structures
- Combined income pushes couples into higher federal brackets faster
- Family credits phase out earlier
Georgia couples with two incomes will need to plan carefully for the 2026 changes.

Georgia-Specific Tax Considerations
Georgia residents must consider how federal changes affect state-tax calculations.

1. Georgia Uses Federal AGI as a Starting Point
Since Georgia begins its tax calculation from federal adjusted gross income (AGI), any increase in federal taxable income automatically increases state taxable income as well.
- W-2 earners
- Business owners
- Retirees drawing taxable income
- Rental property owners
2. Real Estate & Property Owners Will Feel 2026 Changes
Georgia’s real estate markets — especially in Atlanta, Savannah, Augusta, Columbus, and coastal areas — are experiencing strong appreciation.
2026 impacts include:
- Capital gains from property sales
- Reduced depreciation benefits
- Tighter rental classification rules
- Increased taxable income for STR hosts
- Itemized deductions becoming more relevant
Those with multiple properties or short-term rentals should prepare more aggressively.

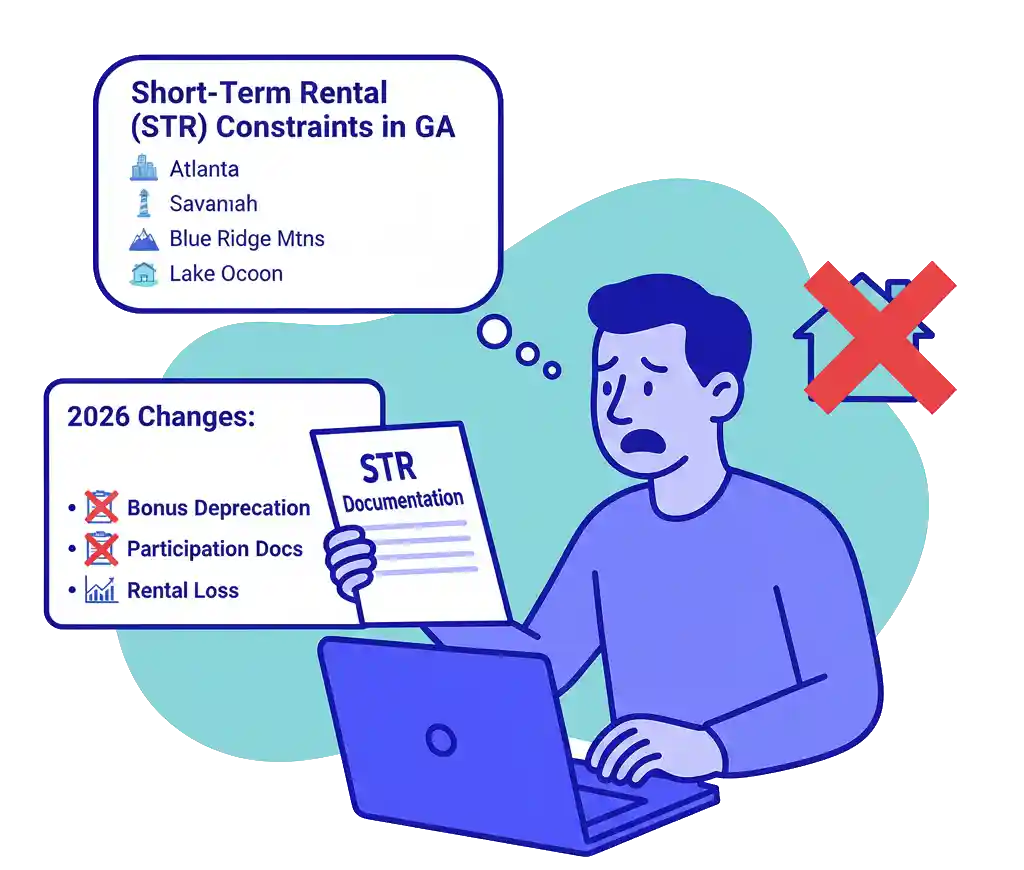
3. Short-Term Rental (STR) Owners Face New Constraints
Popular Georgia STR markets include:
- Atlanta
- Savannah
- Blue Ridge Mountains
- Tybee Island
- Lake Oconee
- Bonus depreciation
- STR participation documentation
- Rental loss treatment
- Active vs passive status
STR owners should expect more restrictive rules and heavier documentation requirements.
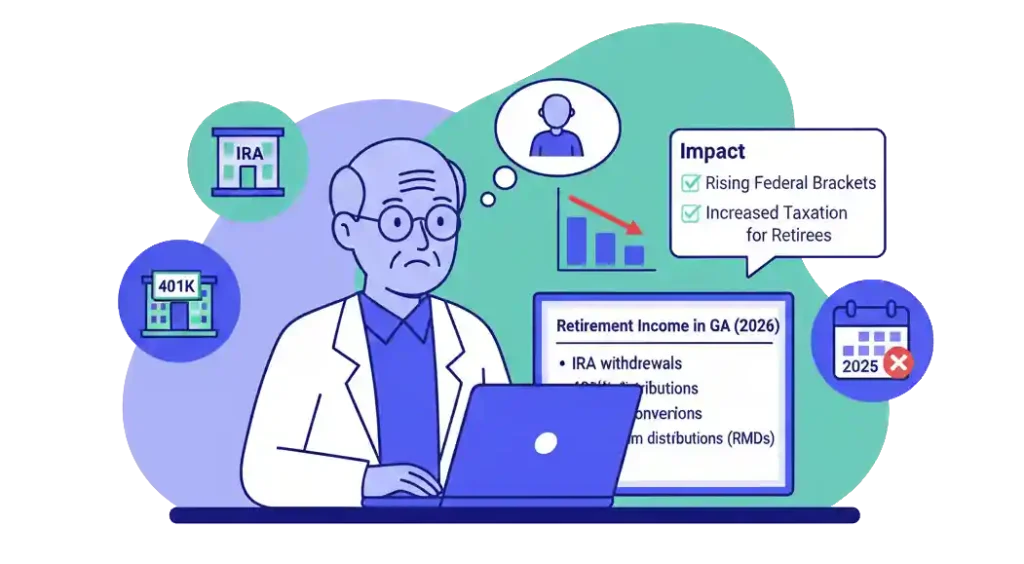
4. Retirement Planning Still Matters Greatly for Georgia Residents
While Georgia excludes portions of retirement income for older residents, federal rules still impact:
- IRA withdrawals
- 401(k) distributions
- Roth conversions
- Required minimum distributions (RMDs)
Rising federal brackets mean retirement taxation may increase for many Georgia retirees.
Who Is Hit Hardest in Georgia (2026)
- Dual-income households
- Homeowners with mortgages
- Business owners (LLCs, S-Corps, contractors)
- Real estate investors and STR operators
- Families with children
- Retirees with taxable retirement income
- Professionals in Atlanta metro
- Self-employed and gig workers

What Georgia Residents Should Do Before December 31, 2025
- Review federal and state withholding
- Maximize retirement contributions
- Consider income timing for 2025 vs. 2026
- Evaluate S-Corp election or business restructuring
- Update documentation for STR or rental activity
- Plan capital gains or property sales carefully
- Consider Roth conversions prior to 2026
- Build a comprehensive 2025–2026 tax strategy
Georgia 2026 Tax FAQ
Does Georgia conform to the QBI deduction?
No — QBI is federal-only.
Will Georgia taxes increase?
Rates stay the same, but federal changes may increase taxable income used by the state.
Are families affected?
Yes — reduced credits and higher brackets increase tax liability.
Are STR owners affected by new rules?
Yes — depreciation, participation tests, and rental loss rules change.
Are retirees impacted?
Yes — federal income tax on retirement distributions can increase.
Get a 2026 Georgia Tax Strategy
Georgia residents face meaningful changes beginning in 2026, including higher taxable income, reduced credits, and adjustments that affect business owners, families, retirees, and investors.
A proactive strategy offers protection and clarity as the new rules take effect.
Because tax situations vary by individual and business, many Georgia residents choose to work with a qualified tax professional. You can explore available Georgia tax services here:
